Evidence shows that lowering blood pressure (BP) decreases the risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes such as heart disease, stroke, and death.1-4 It may also slow the progression of kidney damage in people with chronic kidney disease.5 Further, meta-analyses as well as national and international guidelines suggest that lowering BP decreases risk of these outcomes regardless of which agent is used.1-4,6
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) is a first-line treatment for all stages of hypertension as a monotherapy or in combination with one or more other antihypertensive agents.2,3,6
Monotherapy trials show the BP lowering efficacy of HCTZ.6-15 A 2014 Cochrane Review meta-analysis found 60 randomized controlled trials that studied the dose-related trough BP lowering efficacy of six different thiazide diuretics in 11,262 participants.6 The baseline BP was 155/100 mm Hg across the trials. 33 trials looked at HCTZ specifically. The analysis found mean BP lowering effect over the dose range 6.25 mg, 12.5 mg, 25 mg, and 50 mg/day is -4/-2 mmHg, -6/-3 mmHg, -8/-3 mmHg and -11/-5 mmHg, respectively.
References
- Ahluwalia M, Bangalore S. Management of hypertension in 2017: targets and therapies. Curr Opin Cardiol 2017; 32 (4): 413-421.
- James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, et al. 2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults. JAMA 2014; 311 (5): 507-520.
- Pignone M, Viera AJ. Blood pressure treatment targets in adults aged 60 years or older. Ann Intern Med 2017; 166 (6): 445-445.
- Qaseem A, Wilt TJ, Rich R, Humphrey LL, Frost J, Forciea MA. Pharmacologic treatment of hypertension in adults aged 60 years or older to higher versus lower blood pressure targets: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians and the American Academy of Family Physicians. Ann Intern Med 2017; 166 (6): 430-430.
- KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int Suppl (2011) 2013; 3 (1): i-150.
- Musini VM, Nazer M, Bassett K, Wright JM. Blood pressure-lowering efficacy of monotherapy with thiazide diuretics for primary hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014; (5): Cd003824.
- Kochar M, Guthrie R, Triscari J, Kassler-Taub K, Reeves RA. Matrix study of irbesartan with hydrochlorothiazide in mild-to-moderate hypertension. Am J Hypertens 1999; 12 (8 Pt 1): 797-805.
- McGill JB, Reilly PA. Telmisartan plus hydrochlorothiazide versus telmisartan or hydrochlorothiazide monotherapy in patients with mild to moderate hypertension: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trial. Clin Ther 2001; 23 (6): 833-850.
- Benz JR, Black HR, Graff A, Reed A, Fitzsimmons S, Shi Y. Valsartan and hydrochlorothiazide in patients with essential hypertension. A multiple dose, double-blind, placebo controlled trial comparing combination therapy with monotherapy. J Hum Hypertens 1998; 12 (12): 861-866.
- Canter D, Frank GJ, Knapp LE, Phelps M, Quade M, Texter M. Quinapril and hydrochlorothiazide combination for control of hypertension: assessment by factorial design. Quinapril Investigator Group. J Hum Hypertens 1994; 8 (3): 155-162.
- Chrysant SG. Antihypertensive effectiveness of low-dose lisinopril-hydrochlorothiazide combination. A large multicenter study. Lisinopril-Hydrochlorothiazide Group. Arch Intern Med 1994; 154 (7): 737-743.
- Jounela AJ, Lilja M, Lumme J, et al. Relation between low dose of hydrochlorothiazide, antihypertensive effect and adverse effects. Blood Press 1994; 3 (4): 231-235.
- Lucas CP, Morledge JH, Tessman DK. Comparison of hydrochlorothiazide and hydrochlorothiazide plus bevantolol in hypertension. Clin Ther 1985; 8 (1): 49-60.
- Pool PE, Applegate WB, Woehler T, Sandall P, Cady WJ. A randomized, controlled trial comparing diltiazem, hydrochlorothiazide, and their combination in the therapy of essential hypertension. Pharmacotherapy 1993; 13 (5): 487-493.
- Ernst ME, Carter BL, Zheng S, Grimm RH, Jr. Meta-analysis of dose-response characteristics of hydrochlorothiazide and chlorthalidone: effects on systolic blood pressure and potassium. Am J Hypertens 2010; 23 (4): 440-446.
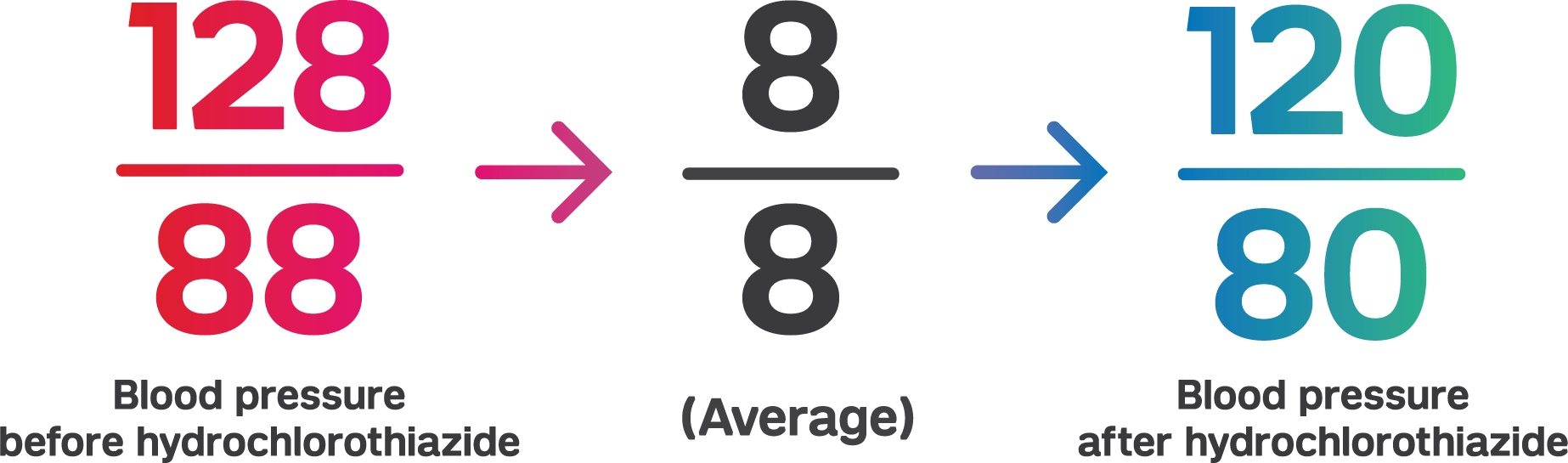

.png)